Brightspace uses a two-site model to streamline subject management: master sites and subject sites. This article explains their purposes, how they differ, and provides tips for managing content, updates, and best practices for their use.
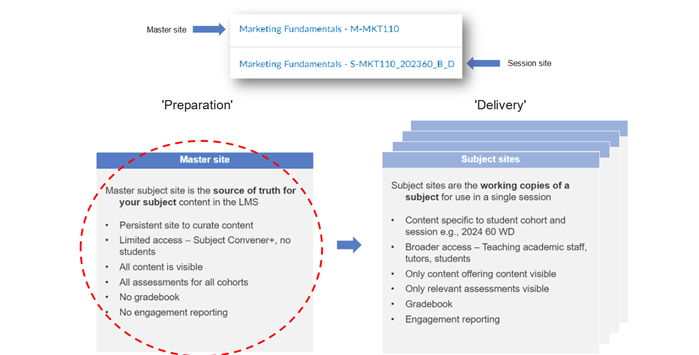
Master sites act as templates for subjects. They are the source of the essential/core learning materials, activities, assessment shells, and marking rubrics that remain consistent across multiple subject offerings throughout the academic year. They provide a validated and up-to-date version of learning materials and assessment, which will be used each teaching period ensuring consistency and version control.
Subject sites are sites for individual teaching periods created from a master site. Academics can customise these sites to cater to the specific needs of a particular teaching period or student cohort. So, while essential readings or topic content may be created in a master site, specific tutorial meetings and recordings may be created and stored in a subject site. They can be thought of as a photocopy of the Master site that is used in the designated teaching period. In the subject site, you can customise content and assessment for that offering if needed.
So, broadly speaking, master sites are used for preparation and subject sites are used for teaching.
| Site | Code | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Support Site | A- | Large enrolments that extend beyond a specific course. |
| Course Site | C- | Enrolment managed by Course of Study (DEEWR) code. |
Organisation Site | O- | Flexible sites that are not connected to grade transfer or Banner enrolments. |
External Site | E- | Offered to external parties via Course Merchant |
Master sites are designated as M- and subject sites are designated as S- within Brightspace. For example, M-ABC101 is the Master site for ABC101, while S-ABC101_202530 is the 202530 subject site for the subject.
Subject conveners have access to and can edit a subject Master site. They can enrol other staff as necessary.
Subject sites will be available to teaching staff, appropriate support staff, and students.
Subject sites are provisioned 4 weeks prior to the start of a teaching period.
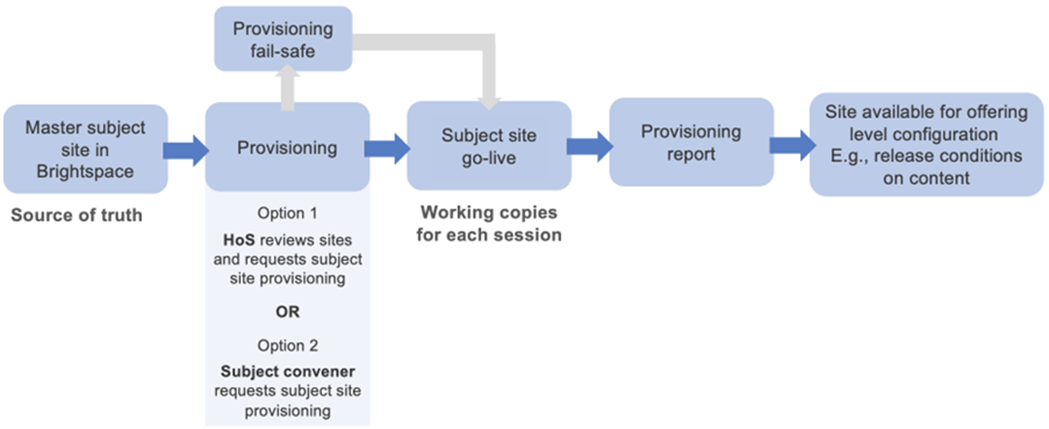
A copy of the master site for each required teaching period (e.g., 202460) will be created.
Within that subject site, we can utilise the Brightspace ‘sections’ feature to provision required elements of the subject to distinct cohorts enrolled in the subject (e.g., Assessment, content and class lists). For example, if a subject has 3 offerings for a teaching period, a subject site could be ACC100_202460 and then 3 sections will be created within that subject site for each of the offerings.
It is recommended that your core content is made ready in your master site before the subject sites are provisioned.
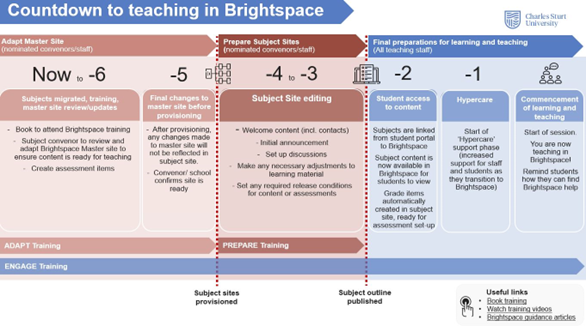
The process will happen as described below, with the preferred method of provisioning at the discretion of the Head of School.
You can choose to provision your subject site early, up to 6 months before the session start date. Before doing so, please ensure the master site is ready as it will be copied automatically.
You will then have to manually update the starting date to release the site to students (if required).
Please note: Not all roles have permission to do this.
If it is necessary to make changes to the core content of the subject during a teaching period, you may need to incorporate those changes back into the master site, so they are available in future subject offerings.
For small amounts of content, we recommend that you simply copy and paste your changes back into the master site.For more information on how to do this, see Copy content.
If you require any assistance, please Log a Service Request.
Assessment setup is a process that works across the Master and Subject sites. Assessment shells are created initially in the Master site, then further refined/contextualised with specific session details in the Subject site.
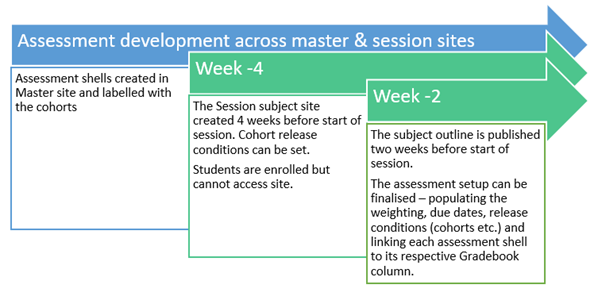
The Master subject site is where the initial assessment ‘shells’ for the subject are created.
When creating assessment shells, no date conditions, cohort restrictions, or task weightings are put in place – this information is later provided within the Subject site.
Assessments created in the Master site should be labelled with the intended cohort if applicable (e.g., Bathurst Distance / BD in brackets etc.)
At week -4, a snapshot is taken of the Master and this new copy becomes the Subject site to be used for the upcoming teaching session – taking on the session code as part of its title (e.g., S-MED111_202431). From this point on, any further development intended for the subject must be done within the newly provisioned Subject site.
The Subject site is the ONE single site created for delivery to ALL cohorts.
At this point, all students are enrolled on the site (but cannot see it yet), with the ‘sections’ for each cohort automatically created based on the students. With sections in place, assessment items that need to be targeted can then be adjusted – using release conditions. All cohorts will see all assignments unless these conditions are put in place. So, at this point, the assignments can be restricted to be visible only to their individual cohorts if applicable.
At week -2, the subject outline is published, creating the full series of columns in the gradebook, 1 for every cohort and for every assessment.
At this juncture the assessment setup can be finalised – populating the weighting, due dates, and most importantly, linking each assessment shell to its respective Gradebook column.
Students get access to the subject, and the published outline (they only see the outline for their relative cohort), whereas the convenor can see all outlines.
This page may be updated at any time. If you print it, you could miss future changes. Please check this page regularly for the latest updates.