The Weed Manager’s Guide To Remote Detection
- Home
- About us
- Detecting weeds
- Get involved
- Resources
Now searching for:
RGB is the most commonly available sensor and as humans are naturally good at perceiving colors, these types of images are easy for us to understand.
RGB sensors
RGB imagery can be found in two main forms: pure images (typically .jpg or .png files) and stitched orthomosaics. Stitched orthomosaics are high-resolution images that are created by stitching together multiple overlapping images. The stitching process removes distortions caused by the camera lens and the Earth's curvature, resulting in a geometrically accurate image with a uniform scale.
Geonadir : What is an othomosaic? Explanations on orthomosaics, their features and functions
The term “RGB” refers to the red-green-blue channels that an image has. These three colours can be combined to create a wide range of colors, which is why RGB images are so commonly used in photography and computer vision applications. Each pixel in an RGB image has three intensity values, representing the amount of red, green, and blue light that is emitted or reflected by that pixel.
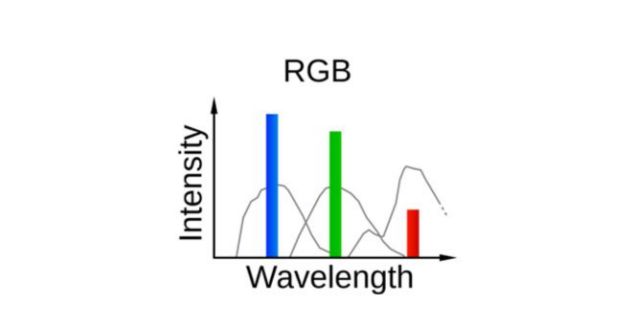
The image is recorded digitally by storing these intensity values for each pixel. RGB sensors are suitable when detecting weeds that are very different to surrounding vegetation. For example, it is highly suitable for hawkweed and bitou bush detection, where flowers look very different to neighbouring plants and can be identified easily in the imagery. Resolution becomes very important in this case, to identify differences between the target plant and surrounding vegetation or lookalike species.
Geonadir : Types of environmental sensors for drones describes the principles behind the sensors that capture this imagery. Scroll to the discussion on RGB sensors and the electromagnetic spectrum: